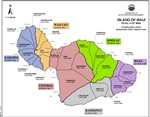
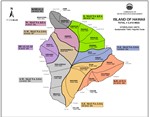
Hydrologic Units
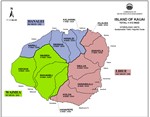
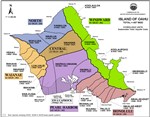
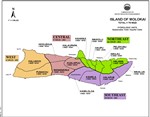
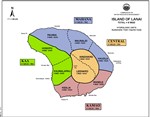
Ground-water hydrologic units have been established by the Commission on Water Resource Management to provide a consistent basis for managing ground water resources. The units are primarily determined by subsurface conditions. In general, each island is divided into regions that reflect broad hydrogeological similarities while maintaining hydrographic, topographic, and historical boundaries where possible. Smaller sub-regions are then delineated based on hydraulic continuity and related characteristics. In general, these units allow for optimized spreading of island-wide pumpage on an aquifer-system-area scale.
An aquifer coding system is used to reference and describe the ground water hydrologic units delineated by CWRM. It is established to provide a consistent method by which to reference and describe ground water resources, and to assist in various water planning efforts. The coding system was first initiated by the State Department of Health in response to directives from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Since then, boundary delineations of ground-water hydrologic units were manually drawn or retraced by the DLNR Division of Water and Land Development (DOWALD) General Flood Control Plan of Hawaii (1983), the State Department of Health (1987), and the Commission on Water Resource Management (1990).
Please refer to the current Water Resource Protection Plan (WRPP) for more information on the ground water hydrologic units.