(Lihue)-Detection of Ceratocystis lukuohia, the more virulent of the two fungal pathogens causing Rapid ʻŌhi‘a Death (ROD), has now been confirmed in three trees on Department of Hawaiian Home lands parcel behind Kalalea Mountain on the east side of Kaua‘i. This first detection of C. lukuohia comes after the other pathogen resulting in ROD, Ceratocystis huliohia, was detected on Kauai in three distinct locations this past year.
Invasive Species
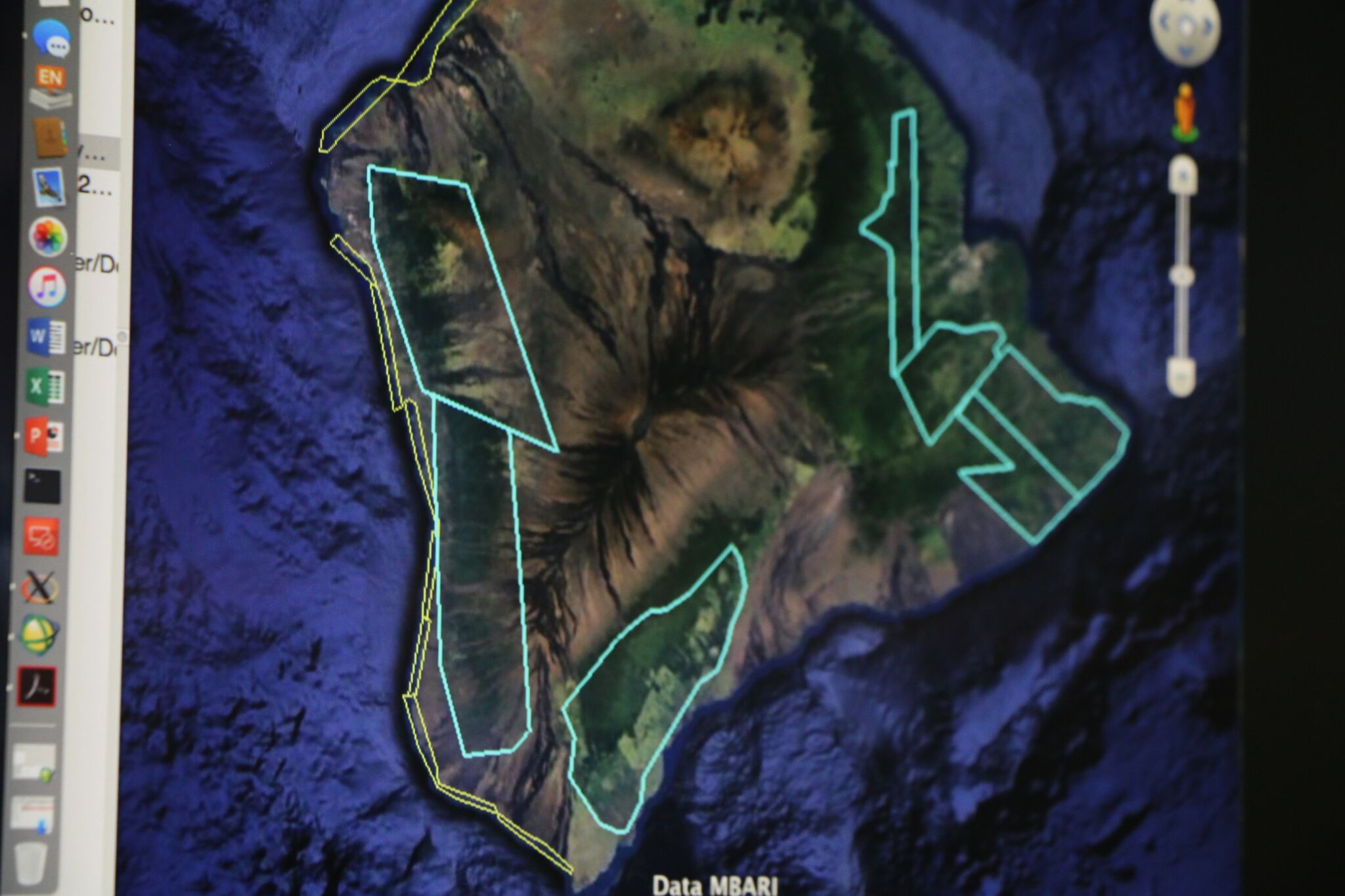
(Lihue) - Rapid ʻŌhi‘a Death (ROD), a disease killing ʻōhiʻa trees, has been confirmed at two new locations on Kaua‘i. Since ROD was discovered in Moloa‘a State Forest Reserve in 14 trees earlier this year, a collaborative team of scientists from state, federal, and private organizations has been working together to survey the island and develop response plans to an introduced disease threat facing Hawai‘i’s native tree. ʻŌhiʻa is considered foundational to Hawaiian forests and culture.
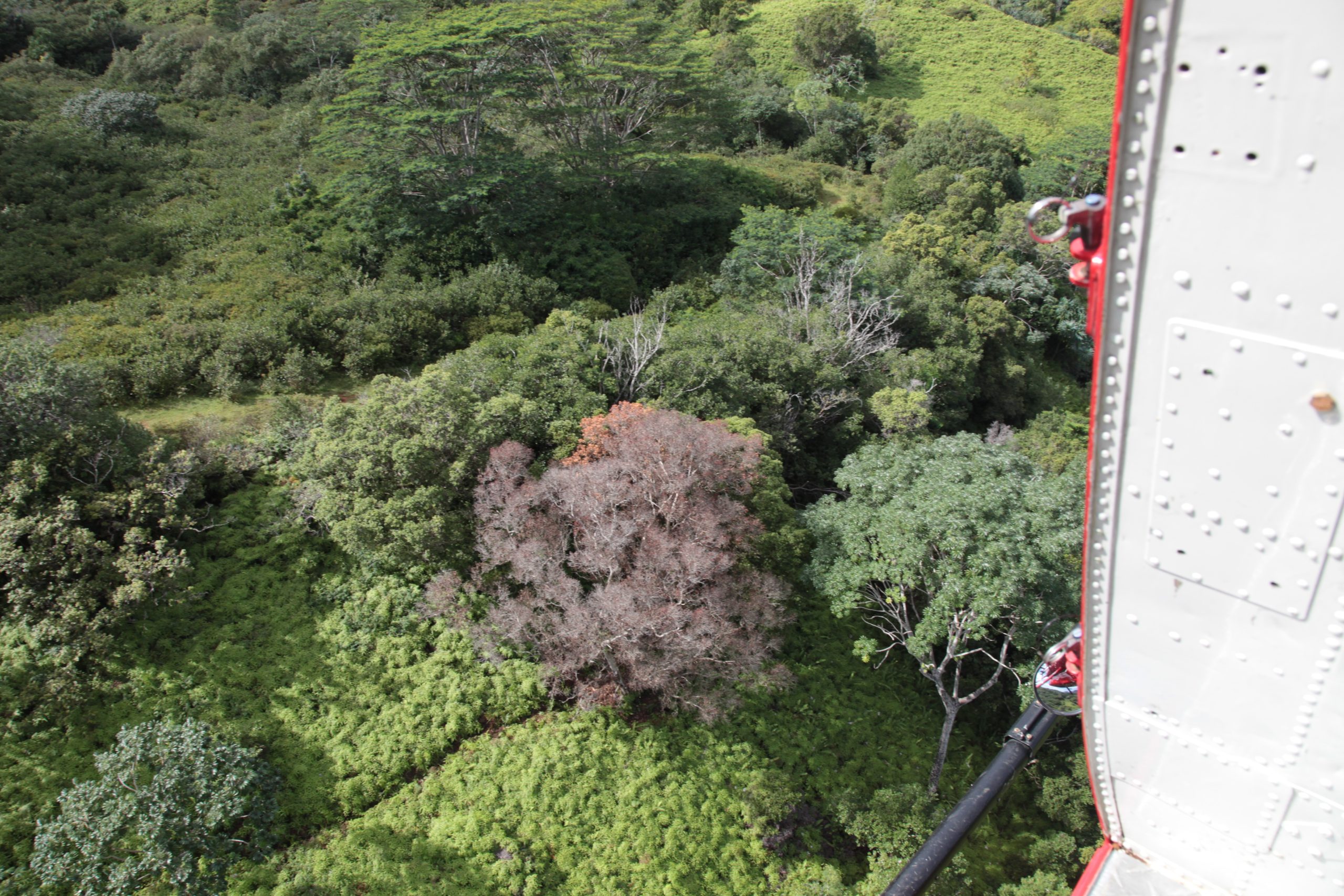
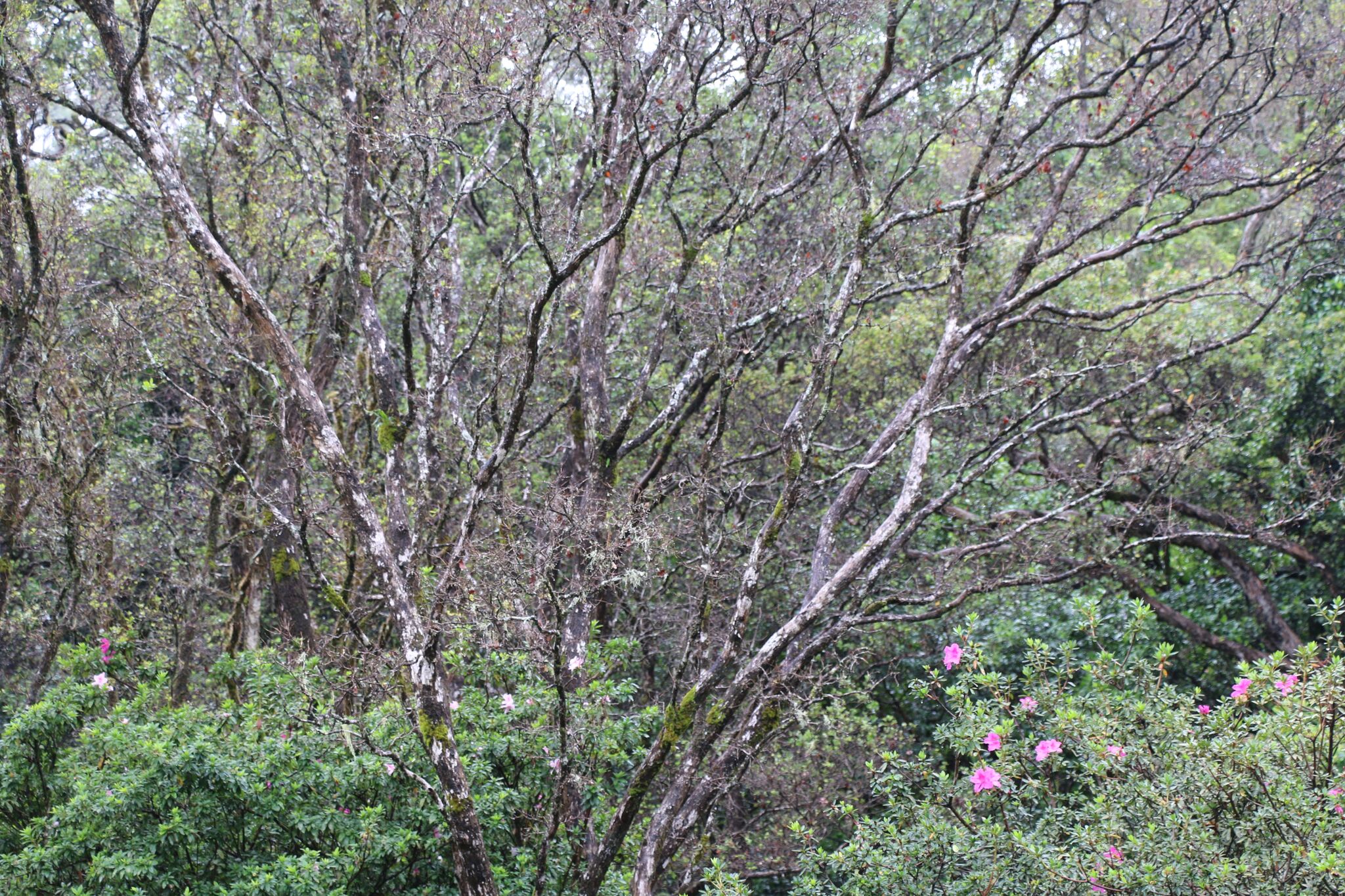
(Hilo) - Next week staff from the Big Island Invasive Species Committee, the DLNR Divisions of State Parks and Forestry and Wildlife will be working to fell and remove several `ohi`a trees that show symptoms of the fungal disease known as Rapid ʻŌhiʻa Death (ROD). After the first suspected detection at Kalōpā State Recreation Area in late July, three trees were sampled in the park and three in an adjacent forest reserve. Five of the six samples tested positive for C. lukuohia, one of a pair of fungi associated with Rapid ʻŌhiʻa Death and the most aggressive of the two.
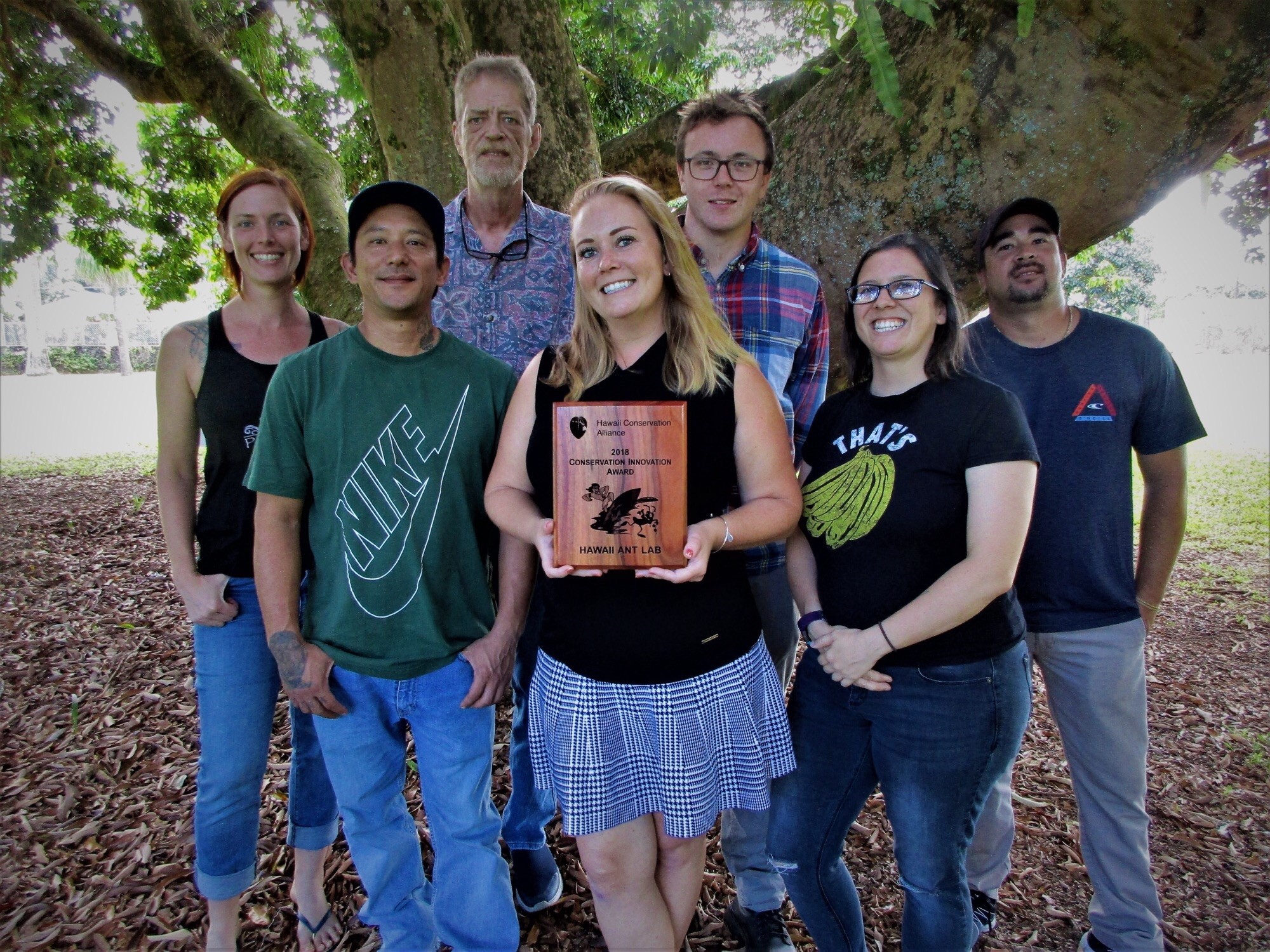
(Hilo) – The Hawaii Ant Lab has won the 2018 Conservation Innovation Award by the Hawaii Conservation Alliance. The Ant Lab is a collaboration of the University of Hawaii’s Pacific Cooperative Studies Unit and the Hawaii Department of Agriculture, and was established in response to the Little Fire Ant invasion.
(Hilo) – Rapid ʻŌhiʻa Death (ROD), the fungal disease that’s impacted hundreds of thousands of acres of native ‘ōhi‘a forests in Hawai‘i, is the actual reason for the ʻŌhiʻa Love Festival today at the ‘Imiloa Astronomy Center. Now in its second year, more than a thousand people honored ‘ōhi‘a and the many people working to stop the spread of ROD and find effective treatments for it. The festival goes beyond the disease.
(Hilo) – During a regularly scheduled quarterly aerial assessment of forests on Hawai‘i island in late July, spotters detected more trees “symptomatic” for the presence of C. lukuohia, the fungus more commonly known as Rapid ʻŌhiʻa Death. These trees are in the Kalōpā State Recreation Area on the Hamakua Coast and after the helicopter surveys utilizing digital mobile sketch mapping (DMSM), ground crews from the Big Island Invasive Species Committee (BIISC) followed up by taking ground samples.
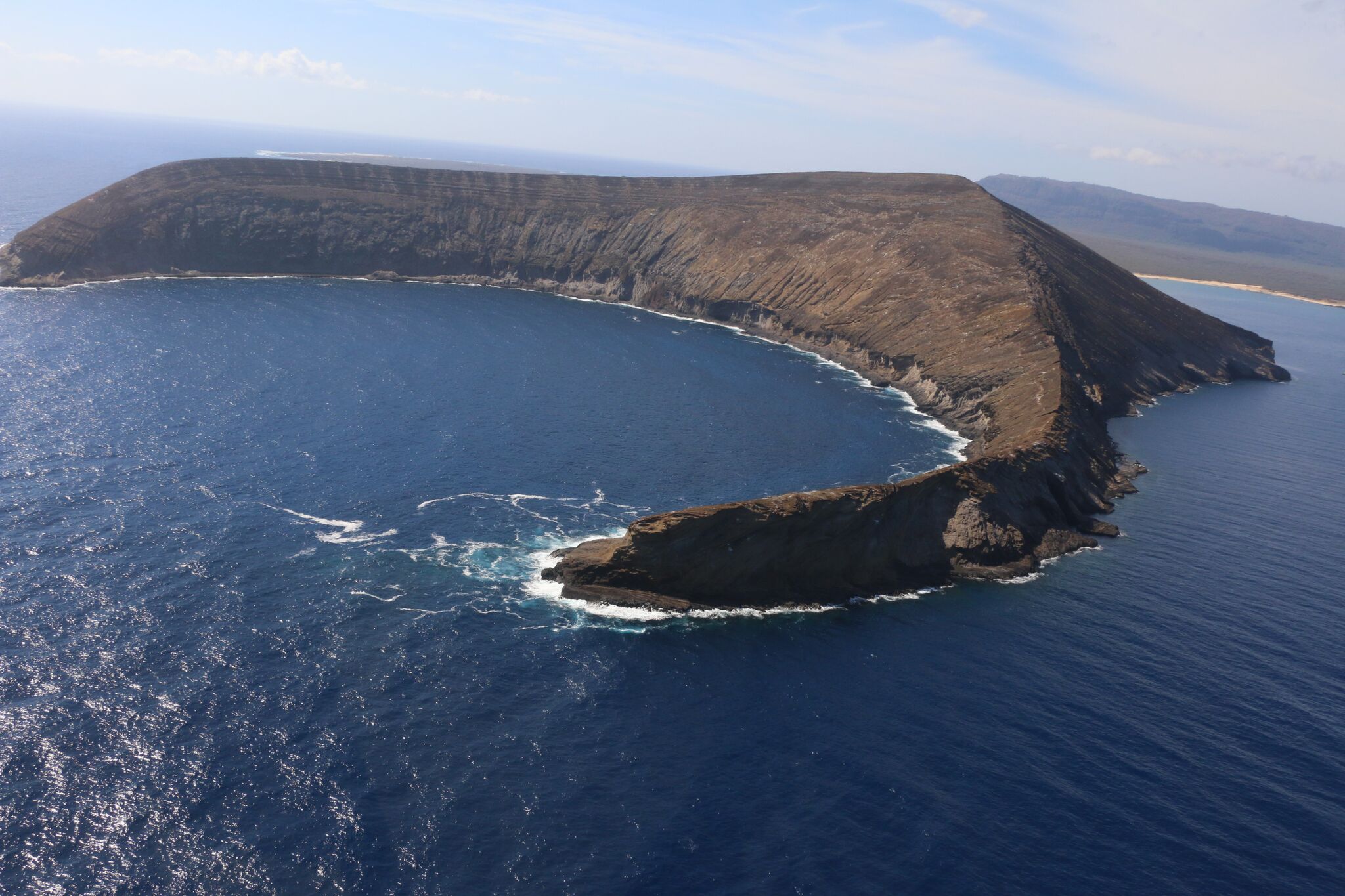
The recent project aimed at eradicating invasive rats from the State of Hawai‘i’s Seabird Sanctuary on Lehua Island is the subject of a half-hour long TV documentary that chronicles the operation from beginning to end. Scheduled for broadcast on KFVE-TV (K5) on Saturday, Oct. 21st and Sunday, Oct. 22nd at 9:30 p.m. and 6:30 p.m. respectively, the program was produced by DLNR with support from the Lehua Island Restoration Steering Committee; the group of government agencies, non-profit and community organizations, and other supporters involved in the eradication of rats.
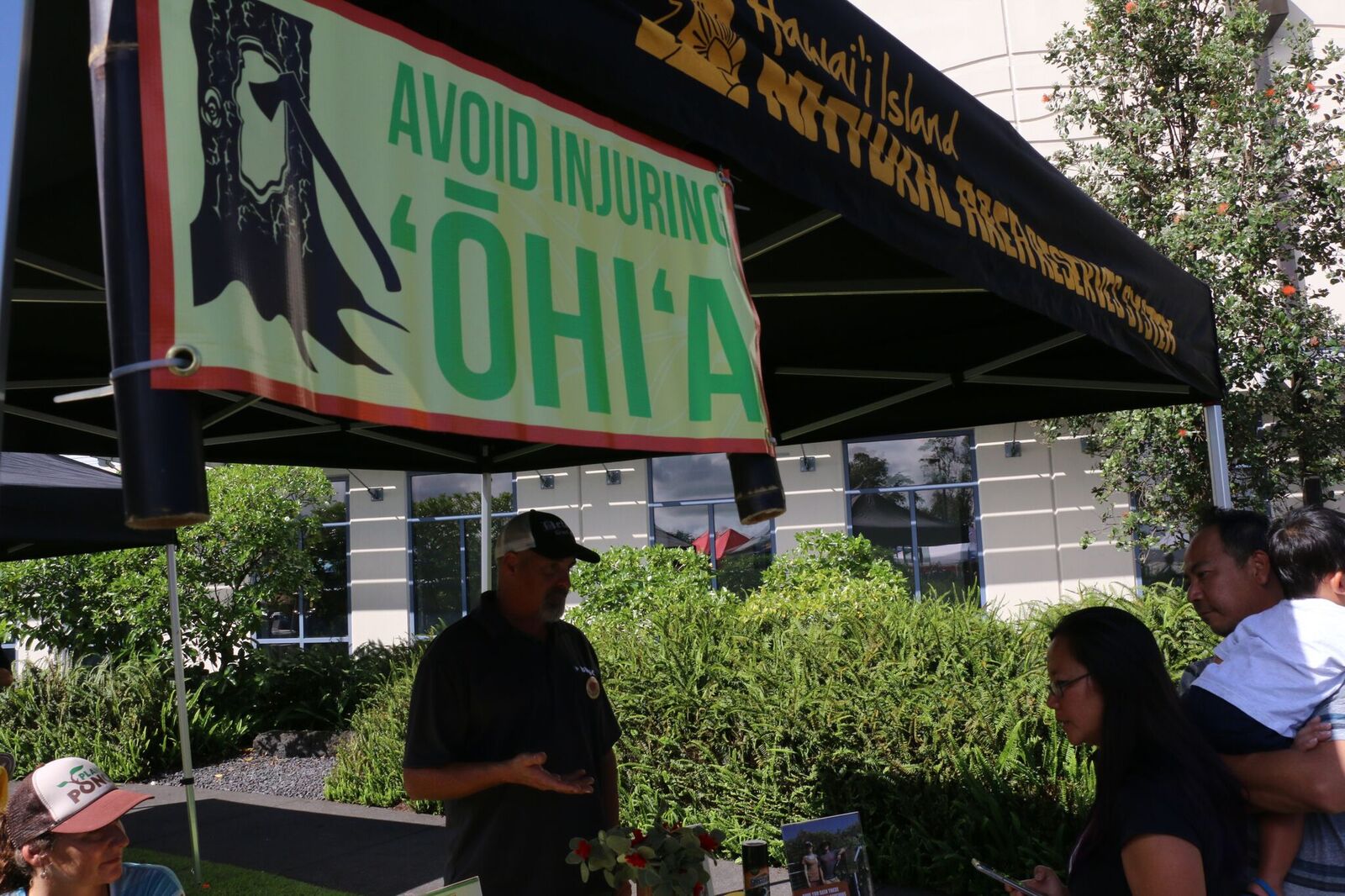
With 75,000 acres of Hawai‘i island ʻōhiʻa forest now showing symptoms of the fungal disease known as Rapid ‘Ōhiʻa Death, federal and state agencies and non-profit partners are using an array of high technology to detect its spread. “The battle against the two types of Ceratocystis fungus that causes Rapid ‘Ōhiʻa Death has always been a hugely collaborative effort,” said Rob Hauff, State Protection Forester for the DLNR Division of Forestry and Wildlife (DOFAW). “Now,” Hauff explained, “the collaboration between the agencies and organizations engaged in the fight against this devastating disease not only continues, but is expanding, particularly on the detection front.” Early detection is considered critical in helping to identify Rapid ‘Ōhiʻa Death’s spread on the Big Island and to other islands and to provide data and scientific information to aide researchers working hard to find a way to stop it.
Governor David Ige proclaimed the 5th annual Hawaii Invasive Species Awareness Week (HISAW) at a ceremony Friday that included agency leaders, legislators, industry champions, and citizens who help project Hawaii from the impacts of invasive species. The Governor presented the proclamation to members of the Hawaii Invasive Species Council (HISC), the interagency board responsible for policy direction and cross-sector coordination on invasive species issues. Addressing invasive species is a critical component of this administration's vision for Hawaii's future, as described in the recent Hawaii Interagency Biosecurity Plan and the Sustainable Hawaii Initiative.
It’s another spectacular sunset near Spouting Horn on Kauai’s south side. As people gather at the shoreline to catch a glimpse of the fabled green flash, their eyes turn inland for the green flash in the sky. This is the nightly invasion of rose-ringed parakeets. Their highly visible presence on the Garden Island provides a current and dramatic example of how a seemingly innocuous species, left unchecked and over time, can become a public health hazard, a real nuisance, and have serious impacts on the economy and the environment.